Framework structure
The key elements of the NMAHP development framework are the:
- Levels of practice
- Pillars of practice
- Knowledge, Skills and Behaviour statements
- Development Needs Analysis Tool
- Framework Reflection Tool
Levels of practice
The levels of practice are based on the Career Framework for Health (Skills for Health 2006; Scottish Government 2009). The levels in the NMAHP & HCSW Development Framework span from level 2 healthcare support worker to level 8 consultant and reflect role development and progression.
Each level has an overview which describes the attributes and the qualifications expected to practice at this level. Generic knowledge, skills and behaviour (KSB) statements are also included for each level to enable you to benchmark and identify any development needs. The consolidation of existing knowledge and skills, and the acquisition of new ones, are reflected in the incremental nature of the framework levels. The KSBs are arranged under the 4 pillars of practice.
It is worth noting that there is a fundamental difference between the Levels of practice described in the Framework and the pay band you are employed at. The Levels reflect career progression and do not link to the Agenda for Change (AfC) pay bands which are related to remuneration and set by your employer.
Go to the Access the Framework page and you will find more information about which level of practice in the overview section.
Pillars of practice
The Framework is structured around 4 interconnected Pillars of Practice. Namely Clinical Practice, Facilitating Learning, Leadership, Service Improvement/ Evidence, Research and Development. The knowledge, skills and behaviours described in the Pillars are common to all NMAHP professions and specialities.
The Pillars and Levels are designed to work together to highlight the breadth and range of knowledge and skills required to practice safely and effectively for all healthcare professionals.

Table 1 gives an overview of the knowledge, skills and behaviours described within each pillar.
| Pillars of Practice | Description |
| Clinical Practice | The knowledge, skills and behaviours needed to provide high quality healthcare that is safe, effective and person centred. |
| Facilitating Learning | The knowledge, skills and behaviours needed to enable effective learning in the workplace |
| Leadership | The knowledge, skills and behaviours needed to lead and to fulfil management responsibilities |
| Service Improvement (Levels 2 to 4) | The knowledge, skills and behaviours needed to use evidence to improve services and practice. |
| Evidence, Research and Development (Levels 5 to 8) | The knowledge, skills and behaviours needed to use evidence to inform practice and improve services |
Using the Pillars
The Pillars are designed to help you look at all aspects of your practice and support your learning and development.
There can be a tendency to focus on the Clinical Pillar initially as the knowledge and skills may feel more relevant and familiar. However, developing skills across the other Pillars can serve to strengthen your clinical skills. The emphasis on each Pillar can vary according to your level of practice and your specific role.
For example, the emphasis may be on the Clinical Practice Pillar for a practitioner at Level 5 whereas at Level 8, the Leadership Pillar may predominate (Figure 1). A practitioner in a specific role, such as a Practice Educator, will give more emphasis to developing the knowledge, skills and behaviours associated with the Facilitating Learning Pillar than a practitioner at the same level working in a clinical role.
Depending on the individual’s role, they may not demonstrate all knowledge, skills and behaviours all of the time, but they should have the capability to do so at their level of practice and all those in the preceding level of practice.
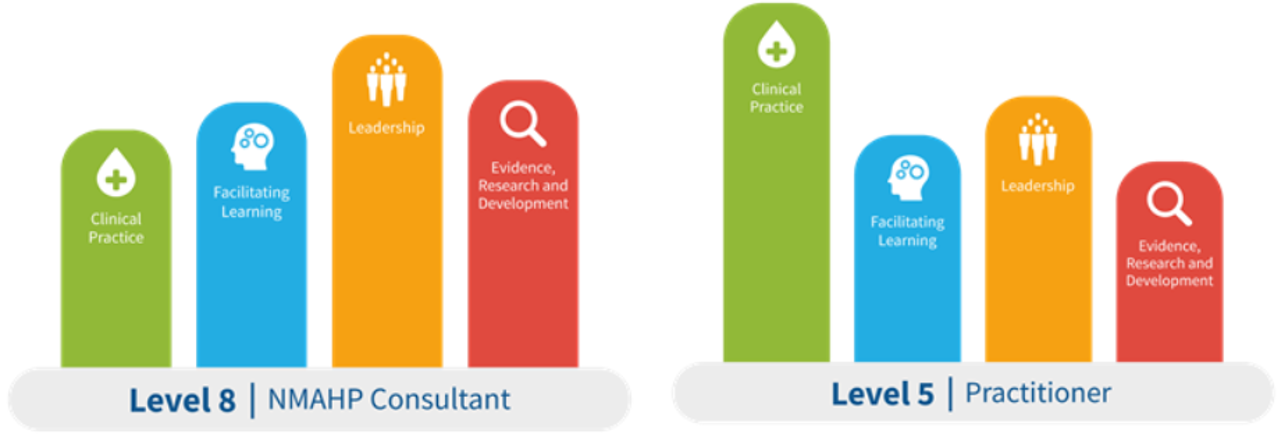
Figure 1

Knowledge Skills and Behaviours
The knowledge, skills and behaviours (KSBs) described in the pillars are common to all NMAHP professions and specialities and can be applied to the specific context in which you work.
The Framework is designed to work in conjunction with other specialist frameworks. The Framework provides the generic/core content, that can be used as the basis from which to add role-specific knowledge, skills and behaviours and the detail associated with a specialism. For example, a practitioner working in a mental health clinical environment may add clinical elements from a specialist mental health framework.
Please note that there are some similarities and overlap of the KSB statements between the Pillars. It is worth keeping this in mind when you are developing your evidence as it may cover several KSBs across the Pillars.
Development Needs Analysis Tool (DNAT)
The Development Needs Analysis Tool (DNAT) is a self-assessment tool that enables you to use the Framework to reflect on your job role and identify areas where you might benefit from further development. The DNAT uses the knowledge, skills and behaviour (KSBs) statements from the Framework which are arranged under the Pillars of Practice to assess your Level of practice. There is a DNAT for each corresponding Level of the Framework.
A RAG (Red-Amber-Green) rating scale is used to help you to assess and rate your current knowledge and skills. Like most forms of self-assessment this can feel a bit daunting and challenging. The best approach is to try to be as open and honest as possible when reviewing each KSB.
RAG scale
|
|
|
RED |
I require training and development in most or all of this area. |
AMBER |
I require further training and development in some aspects of this area. |
GREEN |
I am already confident in carrying out this outcome competently. |
You can individualise the DNAT by adding additional role/profession specific KSBs from other competency frameworks relevant to your role. There is a blank template for this purpose.
The DNAT can also be used to demonstrate evidence of competency to support advanced level practice local Sign-Off and ongoing proficiency.
Once completed the DNAT can be used to support reflective discussions and professional development planning with your manager.
The DNAT can be accessed in different formats to suit your learning needs. You can download as a word document, or you can access an online version of the tool. The online version can be saved, printed and sent to a third party. To access the DNAT go to the Access the Framework page and select your level of practice and then go to the Self-Assessment subsection.
If you are completing the DNAT in full it will take approximately 3 hours to complete. It is recommended that you complete one pillar at a time then save, this will take approximately 45 minutes to an hour per pillar. To save your responses you need to be signed into your Office 365 account. For more information on how to do this, please read this guidance.
Framework Reflective Self-assessment Tool
This reflective self-assessment tool is designed to help you evaluate the knowledge, skills, and behaviours (KSBs) outlined in the Framework for your level of practice. It encourages you to reflect on your job role, identify areas for potential growth, and recognise opportunities for further development.
The 4 Pillars of Practice provide a framework to guide your reflection. For Levels 2 to 4, the pillars include Clinical Practice, Facilitation of Learning, Leadership, and Service Improvement. For Levels 5 to 8, the pillars shift to Clinical Practice, Facilitation of Learning, Leadership, and Evidence, Research, and Development.
If you are new to reflection, there is a helpful guidance section with tips and activities to help you to reflect.
This tool serves as an alternative to the Framework Development Needs Analysis Tool (DNAT).
Once completed the tool can be used to support reflective discussions and professional development planning with your manager. If you are working at advanced level the tool can also be used to support evidence of competence and sign off locally.
The Reflective Self-assessment Tool is in MS Word format and is accessed via a link in the Self-Assessment page of your level. You can download and save this self-assessment tool, allowing you to input directly into the document to complete the required sections. Alternatively, you can print this document and write your response by hand. The tool will take at least an hour or more to complete.

